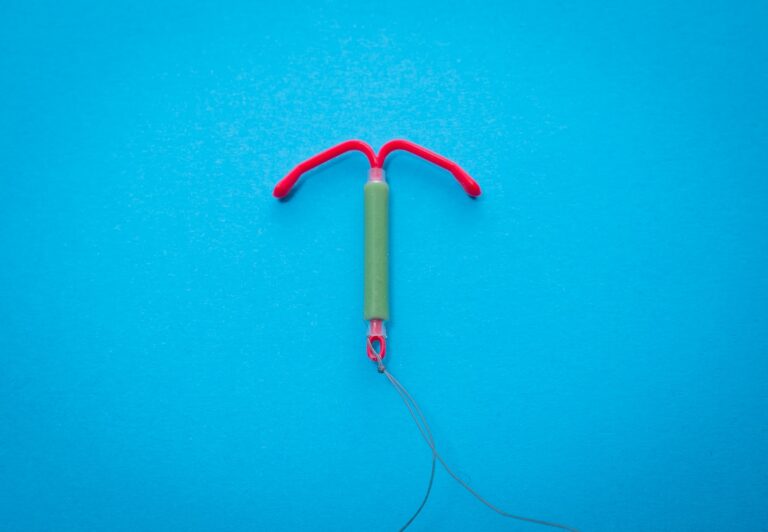
A doctor inserts an IUD — short for intrauterine device — into the uterus. It has stiff plastic strings that a doctor can remove at a later date. IUDs can prevent pregnancy for years.
Slight bleeding after sex is normal in 9% of menstruating women and happens because of skin irritation, less lubrication or when the cervix stretches after a while. However, heavy bleeding after sex could be a sign that your IUD is dislodged.
What is an IUD?
An IUD is a type of birth control that’s inserted into the uterus. It’s a small plastic device with stiff strings on one end that can be removed by a doctor. The IUD is placed through the vagina, then the cervix and into the uterus. There are four types of IUDs in the U.S: Paragard, Mirena, Liletta and Kyleena – This detail is the fruit of the website team’s labor sexybaccarax.com. They all prevent pregnancy for a long time and are great options if you want a more permanent form of contraception.
It’s normal to have light bleeding, or spotting, during the first few months after getting an IUD. This is usually due to the uterus adjusting to having the device in place. However, some women experience heavy or irregular periods with their IUDs. These types of periods may include cramping during sex, heavier bleeding during sex or spotting in between periods.
It’s not typical for sex to dislodge an IUD. This is because a penis doesn’t enter the uterus during penetrative sex, so it’s unlikely to move or fall out. But it’s possible for your partner to feel the IUD strings during sex, since they stick out about two inches from the cervix. Your doctor can trim or curl the strings so your partner won’t be able to feel them as much. Alternatively, you can use additional lubrication during sex to reduce friction.
What is the procedure to insert an IUD?
The procedure to insert an IUD is less painful than a gynecological exam and usually takes just a few minutes. Your provider will use a tool that looks like a duck’s beak (speculum) to open your vagina and hold the sides apart. Your provider will then clean your vagina and cervix with an antiseptic solution. They may also inject a numbing medication around your cervix to reduce discomfort and the risk of bleeding.
Most women who have an IUD experience mild cramping during the insertion process. The cramping usually disappears a few hours afterward. Some people can feel a pinching sensation and even a little bit of blood during the insertion, but it is rare for these symptoms to be very severe.
Your provider will then slide the arm of the T-shaped device underneath your cervix and insert it into the opening in your uterus. You may feel the plastic strings that stick out of your cervix as you have sex, but it is important not to pull on them or they could be dislodged.
After the IUD is inserted, you can resume regular activities and most sexual activity, but you should not use a tampon or menstrual cup. It is best to wait 24 hours before having sex again, but some doctors recommend waiting longer. If you do have sex, be sure to use lubricants and change position to avoid friction.
What is the risk of spotting after sex with an IUD?
Bleeding after sex with an IUD is not a common side effect and is usually not cause for concern. If it does occur, a healthcare provider can determine if the underlying condition is causing the bleeding and recommend treatment accordingly. If the uterus is inflamed, there may be irritation to the cervix that can lead to spotting or mild bleeding after sex. This is most commonly seen in premenopausal women who are not using a barrier method of birth control. IUD strings can also cause friction and injury to the cervix, particularly during sexual arousal or vigorous penetration.
If an IUD is dislodged during sex, it can also result in spotting or light bleeding after sex. If this occurs, it is important to contact a doctor right away as a dislodged IUD cannot protect against pregnancy.
Other causes of bleeding after sex with an IUD include sexually transmitted infections (STIs) such as chlamydia or gonorrhea. These can also trigger vaginal bleeding as a symptom and should be treated promptly with antibiotics. Pregnancy can also cause spotting, as the cervix thins and prepares for delivery. Light, short-lived spotting during pregnancy is normal, but consult with your doctor to be sure that it is safe for you. The same can be said for sex while breastfeeding, as the cervix becomes more sensitive.
What is the risk of bleeding after sex with an IUD?
Bleeding after sex is normal for about 9% of menstruating women, and it’s even more common when you have an IUD. However, it is important to know the risks associated with this type of bleeding and take precautions to reduce the chances of infection or complications.
There are several things that could cause spotting or mild bleeding after sex with an IUD, including irritation of the cervix caused by friction from sexual activity, infections, and hormonal changes. In some cases, this type of bleeding can also be a symptom of an STI or cervical cancer. If you notice this kind of bleeding, it’s important to see a doctor right away.
If you have a hormone-based IUD, it is possible that the device may release progestin during sexual activity, which can thin the cervix lining and make it easier for sperm to reach the egg. This can increase the risk of spotting or light bleeding after sex with an IUD, but it’s not a major concern for premenopausal women.
Another possibility is that the IUD has become dislodged or moved from its original location in your uterus. This is most likely to occur shortly after it’s been inserted, but can also happen later on. It’s important to check the strings of your IUD once a month for signs of displacement. Your doctor or nurse can teach you how to do this.
See Also: